从零开始:用Flask框架实现一个简单而实用的登录页面
简介
登录验证是私密性较强网页的共同需求,这篇文章提供一个基于FLask的登录验证功能实现。
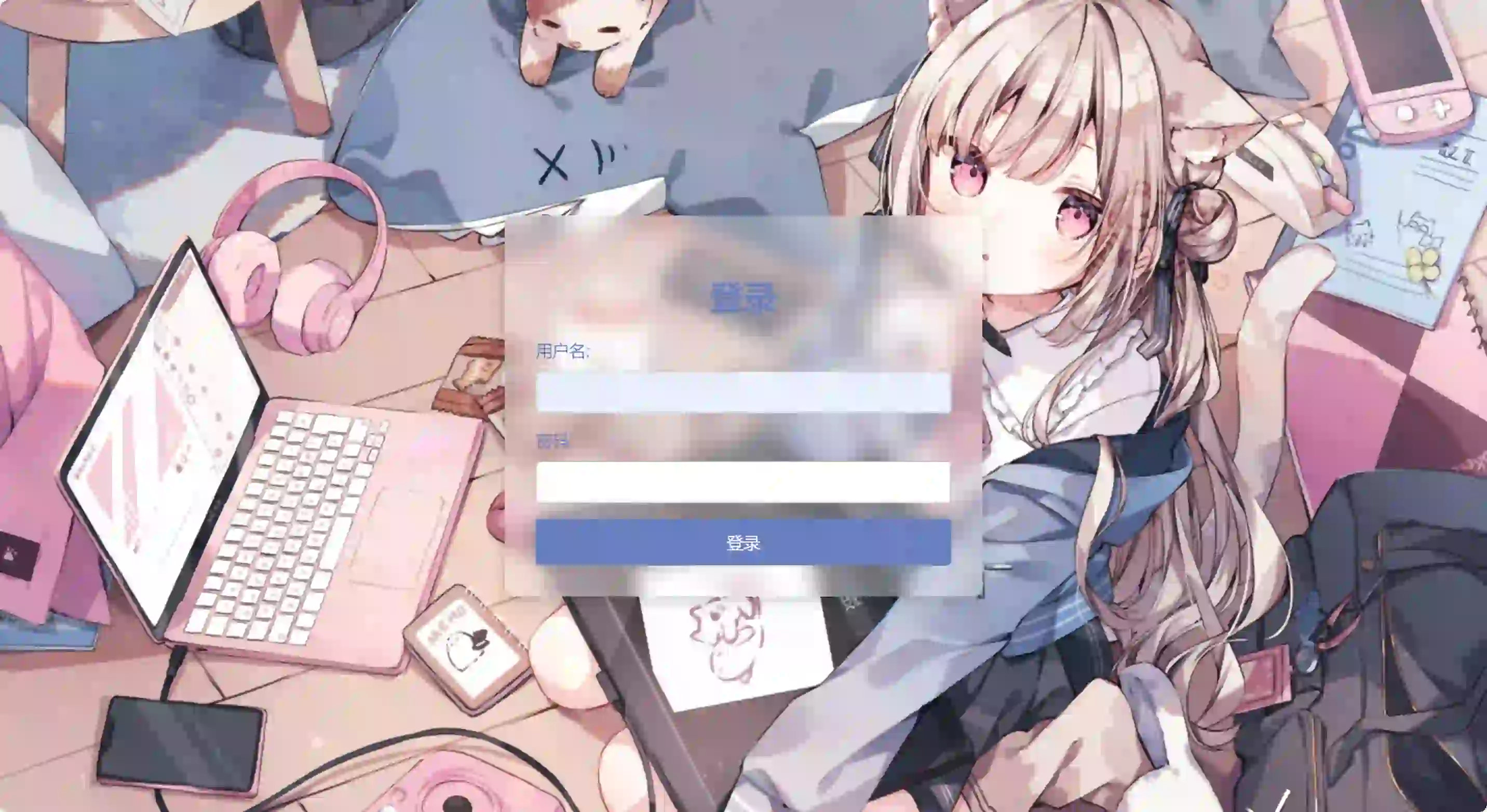
实现
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>登录</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="/static/images/favicon.ico">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="login-container">
<h2>登录</h2>
<form id="loginForm">
<div class="input-group">
<label for="username">用户名:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" required>
</div>
<div class="input-group">
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" required>
</div>
<button type="submit">登录</button>
<p id="error-message" style="color: red; display: none;">用户名或密码错误</p>
</form>
</div>
<script src="/static/js/login.js" async></script>
</body>
</html>登录界面很简单,只有用户名、密码输入框和登录按钮。
CSS
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100vh;
background: url('/static/images/background.jpg') no-repeat center center fixed; /* 设置页面背景 */
background-size: cover;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
/* 登录容器 */
.login-container {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3); /* 半透明背景 */
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 15px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
width: 100%;
max-width: 400px;
text-align: center;
backdrop-filter: blur(10px); /* 背景模糊效果 */
}
/* 标题样式 */
h2 {
font-size: 32px;
color: #697EBF;
margin-bottom: 20px;
font-weight: 600;
}
/* 输入框样式 */
.input-group {
margin-bottom: 15px;
text-align: left;
}
/* 标签样式 */
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 5px;
color: #697EBF;
/*font-weight: bold;
}
/* 输入框样式 */
input[type="text"], input[type="password"] {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
margin-top: 5px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 16px;
box-sizing: border-box;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
/* 输入框聚焦效果 */
input[type="text"]:focus, input[type="password"]:focus {
border-color: #697EBF;
outline: none;
box-shadow: 0 0 8px rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.3);
}
/* 按钮样式 */
button {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
background-color: #697EBF;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #5a79ba;
}
/* 错误信息 */
#error-message {
margin-top: 15px;
font-size: 14px;
color: red;
display: none;
text-align: center;
}
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.login-container {
width: 100%;
max-width: 250px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 24px;
}
}CSS样式没什么好说的,依旧是根据自己的需要修改。
JS
document.getElementById('loginForm').addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
event.preventDefault(); // 防止表单默认提交
const username = document.getElementById('username').value;
const password = document.getElementById('password').value;
// 发送 POST 请求到后端
fetch('/login', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({ username, password }),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.success) {
window.location.href = '/index'; // 登录成功后的跳转界面
} else {
document.getElementById('error-message').style.display = 'block';
}
})
.catch(err => console.error('Error:', err));
});登录函数获取输入的用户名和密码提交到后端进行验证,如果验证成功则跳转到主界面,如果验证失败则显示错误信息。
后端代码
首先实现login函数;
username = os.environ.get('username')
password = os.environ.get('password')
def generate_encrypted_string(username, password):
combined_string = username + password
encrypted_string = hashlib.sha256(combined_string.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest() # 使用 SHA-256 加密
return encrypted_string
@app.route('/login', methods=['POST'])
def login():
data = request.get_json() # 获取前端发送的JSON数据
usn = data.get('username')
pwd = data.get('password')
hashed = generate_encrypted_string(usn, pwd)
# 验证用户名和密码
if hashed == generate_encrypted_string(username, password):
session['logged_in'] = hashed
session['login_time'] = datetime.now(timezone.utc) # 记录登录时间
return jsonify({'success': True})
else:
return jsonify({'success': False, 'message': 'Invalid username or password'})login函数获取用户名和密码组合的哈希值,并与正确的哈希值进行比对,如果登录成功则在浏览器中保存当前哈希值和登录时间。
需要注意的是,用户名和密码不应该在服务器明文保存,正确的做法是在注册用户时将加密后的哈希值保存到数据库中,登录时可以直接比对。由于笔者的用户名和密码是以环境变量的形式存在的,同样没有明文写入代码中,因此省略了这一部分代码。
接下来实现登录跳转代码;
def check_login():
if 'logged_in' not in session or not session['logged_in']:
# 如果没有登录,则重定向到登录页面
return False
else:
logged_in = session['logged_in']
if logged_in != generate_encrypted_string(username, password):
return False
login_time = session.get('login_time')
if login_time:
current_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc) # 使用 UTC 时区的当前时间
if abs(current_time - login_time) > SESSION_TIMEOUT:
session.pop('logged_in', None)
session.pop('login_time', None)
return False
return True
@app.route('/')
def home():
if check_login():
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('login.html') # 返回登录页面
@app.route('/index', methods=['GET'])
def index():
# 处理登录逻辑
if not check_login():
return redirect(url_for('home'))
# ……业务逻辑
passcheck_login函数用于检测用户是否已经登录;home和index都是网站的入口路由,需要在函数头部添加登录逻辑。
最后完成退出登录代码;
@app.route('/logout')
def logout():
# 注销登录,清除 session
session.pop('logged_in', None)
session.pop('login_time', None)
return redirect(url_for('home')) # 重定向到登录页面退出登录的JS代码如下:
function logout() {
fetch('/logout', {
method: 'GET',
credentials: 'same-origin' // 保证请求时带上当前的 session 信息
})
.then(response => {
if (response.ok) {
window.location.href = '/'; // 重定向到登录页面
} else {
alert('退出失败,请稍后再试');
}
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('退出时发生错误:', error);
alert('退出失败,请稍后再试');
});
}随便找个按钮调用logout函数就可以实现退出登录功能了。
从零开始:用Flask框架实现一个简单而实用的登录页面
https://blog.nasxyz.top/archives/fb9bd38c-0312-49cf-8c2a-cb289bddfbe9